Introduction
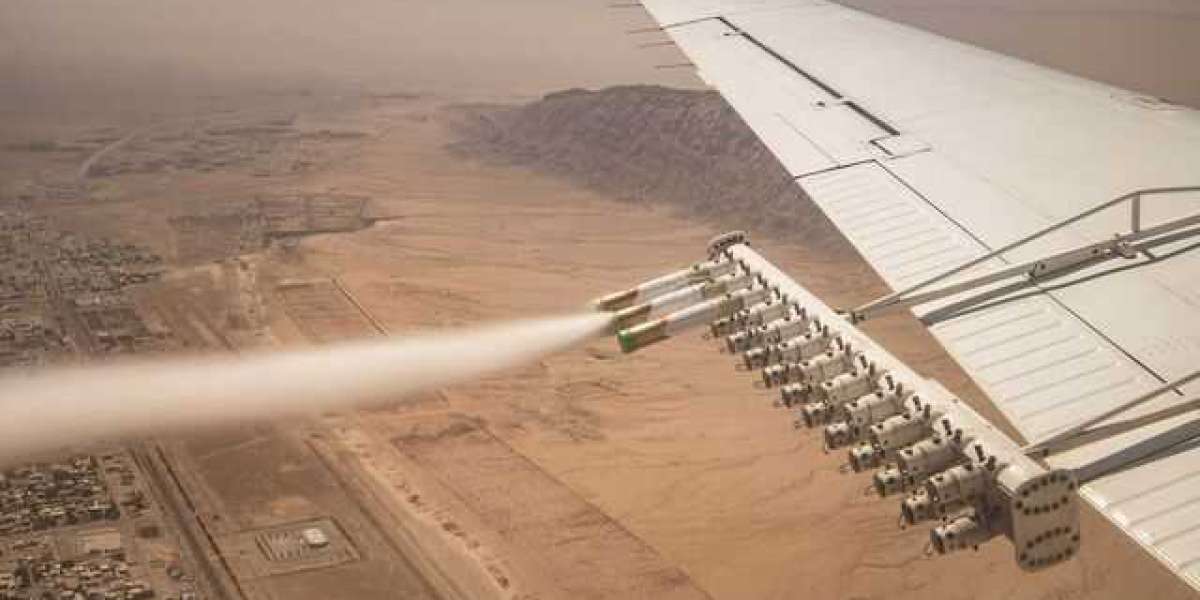
The Cloud Seeding Market focuses on weather modification technologies designed to enhance precipitation by introducing substances into clouds to stimulate rainfall or snowfall. Cloud seeding is primarily used to address water scarcity, improve agricultural productivity, mitigate drought impacts, and support hydropower generation. Common seeding agents include silver iodide, potassium iodide, salt compounds, and dry ice, which encourage cloud droplets or ice crystals to grow and fall as precipitation. As climate variability intensifies and freshwater stress increases globally, cloud seeding is gaining attention as a supplementary water management and climate resilience solution.
Market Drivers
One of the primary drivers of the Cloud Seeding Market is increasing water scarcity. Rapid population growth, urbanization, industrial expansion, and climate change are placing immense pressure on freshwater resources. Many regions are experiencing prolonged droughts and declining groundwater levels, prompting governments to explore cloud seeding as a means to augment water supply for agriculture, drinking water, and reservoirs.
Agricultural demand is another major growth driver. Farming communities depend heavily on predictable rainfall, and erratic weather patterns can significantly impact crop yields. Cloud seeding programs are being adopted to enhance rainfall during critical growing periods, helping stabilize food production and reduce economic losses in agriculture-dependent regions.
Government support and public-sector initiatives also contribute to market growth. Several countries and regional authorities fund cloud seeding programs as part of broader water resource management and climate adaptation strategies, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions.
Market Challenges
Despite its potential, the Cloud Seeding Market faces several challenges. Scientific uncertainty remains a key concern, as the effectiveness of cloud seeding can vary depending on cloud type, atmospheric conditions, and seeding methods. Measuring direct cause-and-effect outcomes is complex, making it difficult to guarantee consistent results.
Environmental and regulatory concerns also pose challenges. The use of chemical agents such as silver iodide raises questions about long-term ecological and health impacts, even though concentrations used are generally low. Regulatory approvals and public acceptance can influence the deployment of cloud seeding programs.
High operational costs represent another challenge. Cloud seeding requires specialized aircraft, ground-based generators, meteorological expertise, and continuous monitoring, which can limit adoption in regions with constrained budgets.
Market Opportunities
Technological advancements present significant opportunities for the Cloud Seeding Market. Improvements in meteorological modeling, satellite monitoring, and weather radar systems are enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of seeding operations. These technologies allow better identification of suitable cloud conditions and optimize seeding timing and location.
Integration with climate adaptation and water management strategies offers additional growth potential. Cloud seeding is increasingly being combined with desalination, water recycling, and conservation programs to create more resilient and diversified water supply systems.
Emerging markets in water-stressed regions present strong opportunities. Countries in the Middle East, parts of Asia-Pacific, and Africa are investing in cloud seeding to support agriculture, replenish reservoirs, and reduce dependence on energy-intensive water solutions.
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific is a major market for cloud seeding, driven by large-scale agricultural needs, monsoon variability, and government-led weather modification programs in countries such as China and India.
The Middle East is another key region due to severe water scarcity and limited natural freshwater resources. Several countries are actively deploying cloud seeding to enhance rainfall and support water security initiatives.
North America has a well-established market, particularly in the western United States, where cloud seeding is used to increase snowpack for water supply and hydropower generation.
Other regions, including Africa and Latin America, are gradually exploring cloud seeding as part of drought mitigation and agricultural support efforts.
Future Outlook
The Cloud Seeding Market is expected to grow steadily as water stress and climate variability intensify. While cloud seeding is not a standalone solution to water scarcity, it is increasingly viewed as a complementary tool within integrated water resource management frameworks.
Future developments will focus on improving scientific validation, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing operational efficiency through digital technologies and advanced atmospheric research. Increased transparency and data-driven evaluation will help build public trust and regulatory support.
As climate adaptation becomes a global priority, cloud seeding is likely to play a more prominent role in targeted and region-specific water enhancement strategies.
Conclusion
The Cloud Seeding Market offers a proactive approach to addressing water scarcity and climate variability by enhancing natural precipitation processes. Driven by agricultural demand, government support, and growing water stress, the market shows steady growth potential. Although challenges related to effectiveness, cost, and environmental concerns remain, technological innovation and integration with broader water management strategies are strengthening the role of cloud seeding in climate resilience planning.