Introduction
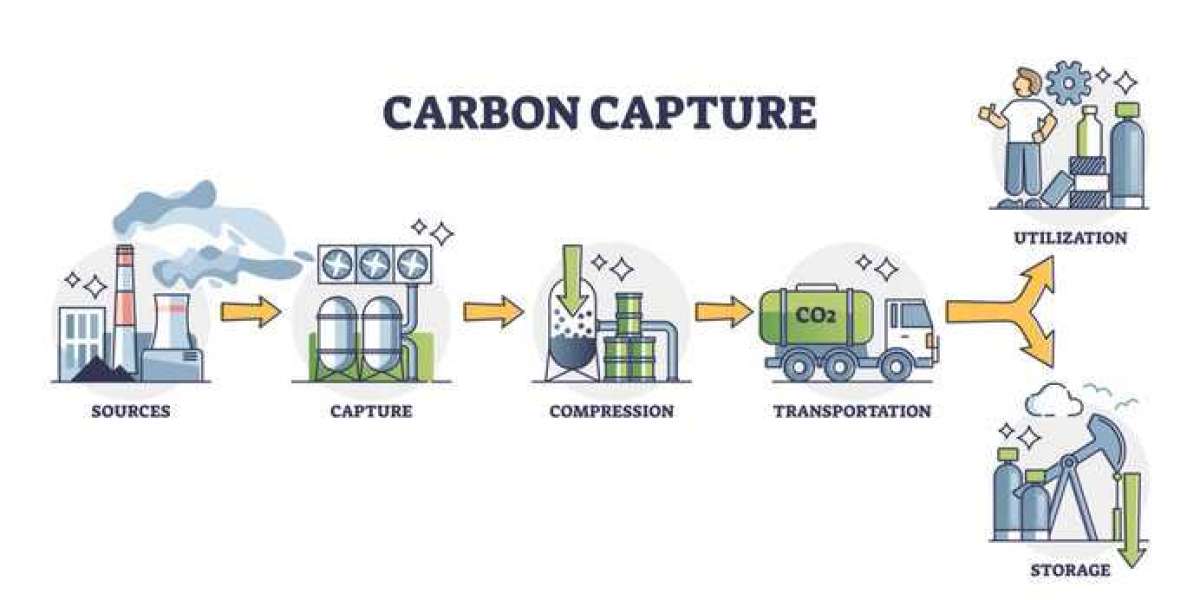
The post combustion carbon capture storage market is gaining strategic importance as industries and governments seek practical solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from existing fossil fuel based infrastructure. Post combustion carbon capture involves removing carbon dioxide from flue gases after fuel combustion, typically from power plants, cement factories, steel mills, and other industrial facilities. This approach is particularly attractive because it can be retrofitted to existing plants without major changes to core production processes. Captured carbon dioxide can be transported and stored in geological formations or utilized in industrial applications. As global climate targets become more stringent, post combustion capture is viewed as a critical bridge technology that enables emission reductions while allowing continued operation of current assets. The market is evolving rapidly as carbon management becomes central to long term decarbonization strategies.
Market Drivers
One of the primary drivers of the post combustion carbon capture storage market is increasing regulatory pressure to reduce carbon emissions from large stationary sources. Governments are implementing emission limits, carbon pricing mechanisms, and net zero commitments that encourage adoption of capture technologies. Post combustion systems are compatible with existing power and industrial plants, making them an attractive option for near term emission reductions. Rising corporate sustainability commitments and environmental, social, and governance requirements further support market demand. Growth in carbon utilization applications, such as enhanced oil recovery and industrial feedstocks, improves the economic viability of capture projects. Public funding, pilot programs, and international climate initiatives also accelerate technology development and deployment. Additionally, hard to abate sectors increasingly rely on post combustion capture to meet emission targets.
Market Challenges
Despite strong policy support, the post combustion carbon capture storage market faces several challenges. High capital and operating costs remain a major barrier, particularly for large scale deployment. Energy consumption required for capture processes reduces overall plant efficiency, increasing operating expenses. Infrastructure limitations related to carbon dioxide transport and storage availability can delay project implementation. Long term liability and regulatory uncertainty around storage sites affect investment confidence. Integration of capture systems with existing facilities requires careful engineering to minimize disruption. Public perception and acceptance of carbon storage projects also influence deployment. Addressing these challenges requires technological innovation, cost reduction, supportive policy frameworks, and development of shared transport and storage infrastructure.
Market Opportunities
The post combustion carbon capture storage market offers significant opportunities driven by innovation and climate policy momentum. Advances in solvent chemistry, membranes, and adsorption materials are improving capture efficiency and reducing costs. Development of modular and standardized capture units enables faster deployment and scalability. Expansion of carbon utilization pathways creates additional revenue streams that enhance project economics. Growth of industrial decarbonization initiatives increases demand for capture solutions beyond the power sector. Emerging markets with expanding fossil based infrastructure present opportunities for early adoption. Collaboration between governments, industry, and technology providers accelerates infrastructure development and knowledge sharing. As carbon markets mature, post combustion capture projects can benefit from credit mechanisms and financial incentives.
Regional Insights
North America represents a leading market for post combustion carbon capture due to strong policy incentives, existing infrastructure, and active pilot projects. Europe shows steady growth driven by climate regulations, industrial decarbonization strategies, and cross border carbon management initiatives. Asia Pacific is an emerging market supported by rising emissions, large coal and industrial capacity, and increasing focus on climate mitigation. Countries in this region are exploring capture technologies to balance energy security and environmental goals. The Middle East is investing in carbon capture to reduce emissions from energy intensive industries and support enhanced oil recovery. Regional growth patterns are shaped by policy support, industrial base, and availability of storage resources.
Future Outlook
The future of the post combustion carbon capture storage market will depend on cost reductions, infrastructure development, and policy stability. Continued research and development is expected to improve efficiency and lower energy penalties. Large scale deployment will be supported by shared transport and storage networks and industrial hubs. Integration of carbon capture with hydrogen production and synthetic fuels may expand application scope. As climate targets tighten, post combustion capture is expected to become a standard component of decarbonization strategies for existing assets. While it is not a standalone solution, it will play a complementary role alongside renewable energy and efficiency measures. Long term growth will be driven by regulatory mandates and global climate commitments.
Conclusion
The post combustion carbon capture storage market is a critical tool in reducing emissions from existing power and industrial facilities. Strong drivers such as regulatory pressure, sustainability commitments, and compatibility with current infrastructure support market growth. Although challenges related to cost, efficiency, and infrastructure persist, technological progress and policy support are addressing these barriers. Opportunities in industrial decarbonization, carbon utilization, and emerging markets enhance long term prospects. As the global energy system transitions toward lower emissions, post combustion carbon capture storage will remain an essential component of comprehensive climate mitigation strategies.