Introduction
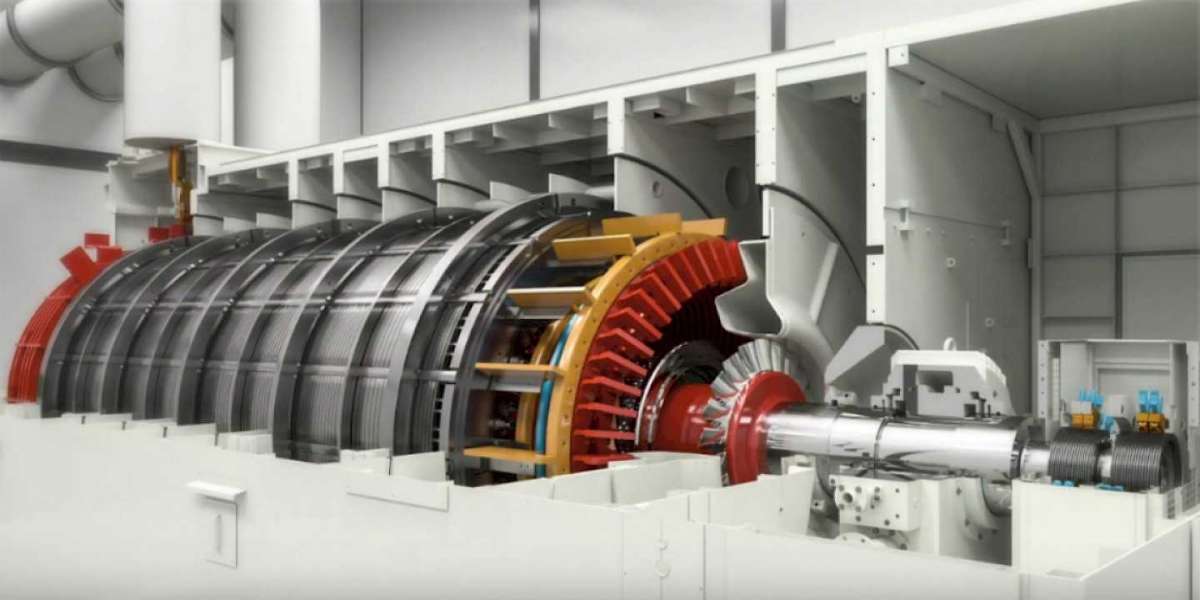
The hydrogen cooled synchronous condenser market focuses on large rotating electrical machines designed to provide reactive power support, voltage regulation, and grid stability without generating active power. These machines are similar in construction to synchronous generators but operate without a prime mover, drawing energy from the grid to stabilize voltage and improve power quality. Hydrogen cooling is used in high-capacity synchronous condensers to efficiently dissipate heat, reduce windage losses, and enable compact, high-performance designs. As power systems evolve with higher renewable energy penetration and reduced inertia from conventional generators, hydrogen cooled synchronous condensers are becoming increasingly important for maintaining grid reliability.
Market Drivers
The market is driven by growing demand for grid stability and reactive power compensation. Increasing integration of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar introduces variability and reduces system inertia, creating a need for fast-responding voltage support solutions. Hydrogen cooled synchronous condensers provide dynamic reactive power, short-circuit strength, and inertia, making them valuable assets for transmission and distribution networks. Expansion of high-voltage transmission lines and interconnections further supports demand, as stable voltage control is essential over long distances. Utilities are also investing in synchronous condensers as older thermal power plants retire, replacing lost grid-support capabilities without adding emissions.
Market Challenges
Despite their technical advantages, hydrogen cooled synchronous condensers face challenges related to cost, complexity, and safety considerations. These systems involve high capital expenditure due to their size, specialized materials, and auxiliary systems such as hydrogen handling, sealing, and monitoring equipment. Operation and maintenance require skilled personnel and strict safety protocols to manage hydrogen safely. Space requirements and long installation timelines can also be constraints, particularly in urban or constrained substations. Additionally, integration with existing grid infrastructure requires careful engineering to ensure compatibility with protection and control systems.
Market Opportunities
The market offers strong opportunities through grid modernization and energy transition initiatives. Many countries are upgrading transmission networks to accommodate renewable energy and cross-border power flows, creating demand for advanced grid support equipment. Replacement of aging power plants with synchronous condensers presents a major opportunity, especially where hydrogen cooling enables high-capacity installations in limited space. Advances in sealing technology, monitoring systems, and automation improve safety and reliability, reducing operational concerns. Emerging markets investing in large-scale renewable projects and high-voltage networks offer long-term growth potential for hydrogen cooled synchronous condenser solutions.
Regional Insights
Regional demand for hydrogen cooled synchronous condensers varies based on grid structure, renewable penetration, and infrastructure investment. Europe represents a significant market due to aggressive renewable energy targets and retirement of conventional power plants, increasing the need for grid stability solutions. North America shows steady growth driven by transmission upgrades and renewable integration, particularly in regions with high wind and solar capacity. Asia-Pacific is a growing market supported by expanding power networks, large-scale renewable projects, and increasing electricity demand in countries such as China, India, and Australia. The Middle East and Latin America present emerging opportunities linked to grid expansion and cross-border interconnections, while Africa remains an early-stage market with future potential.
Future Outlook
The future of the hydrogen cooled synchronous condenser market will be shaped by energy transition dynamics, grid digitalization, and reliability requirements. These machines are expected to play a critical role in supporting low-inertia power systems and ensuring stable operation under high renewable penetration. Integration with advanced control systems and real-time grid monitoring will enhance responsiveness and efficiency. Improved hydrogen management technologies and safety systems will further strengthen adoption. As grids become more complex and decentralized, hydrogen cooled synchronous condensers are likely to remain key assets for maintaining voltage stability and power quality.
Conclusion
The hydrogen cooled synchronous condenser market is a vital segment of modern power system infrastructure, supporting voltage regulation, reactive power compensation, and grid stability. By offering high capacity, efficient cooling, and strong dynamic performance, these systems address challenges arising from renewable integration and generator retirement. While high costs and operational complexity present challenges, ongoing grid modernization and technological advancements continue to drive market demand. As electricity networks evolve toward cleaner and more flexible structures, hydrogen cooled synchronous condensers are expected to remain essential tools for reliable power system operation.
Find similar automotive industry reports offering detailed market insights below:
Automotive Lighting Accessories Market