Introduction
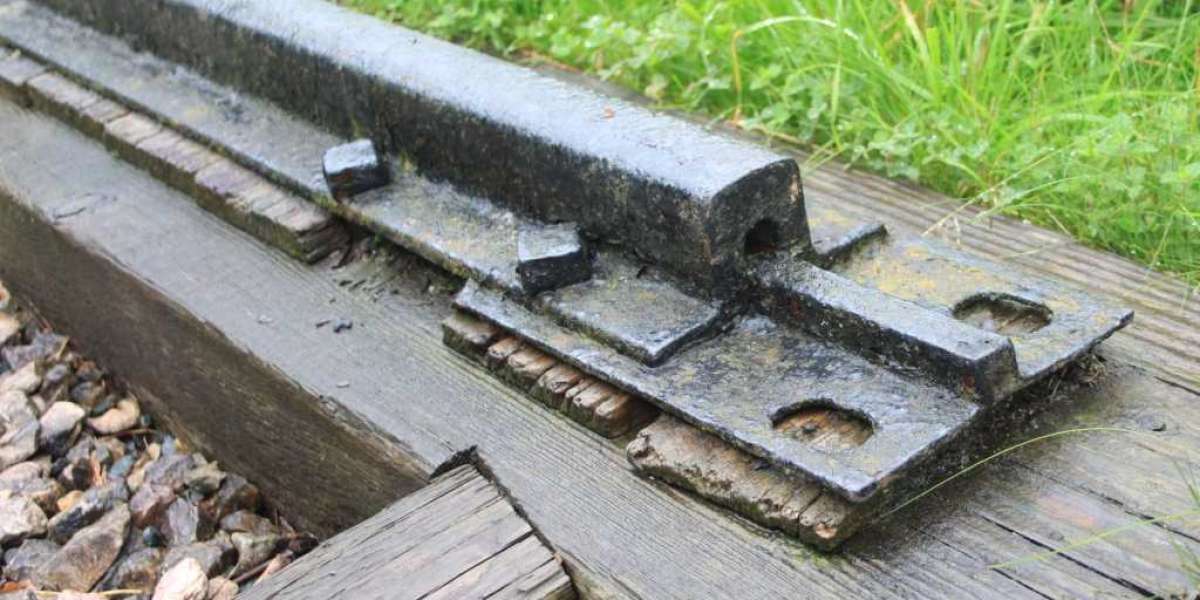
The railway fishplate market focuses on metal joint bars used to connect two ends of railway rails securely and maintain alignment along the track. Fishplates are bolted to rail ends and play a critical role in distributing loads, maintaining track continuity, and ensuring smooth train movement. They are widely used in conventional jointed rail tracks, sidings, yards, and temporary track installations. Despite the growing adoption of welded rails, fishplates remain essential in many rail networks due to their flexibility, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness. As railway infrastructure expands and requires regular maintenance, the demand for reliable fishplate systems continues to remain relevant across global rail operations.
Market Drivers
The market is driven by ongoing railway infrastructure development and maintenance activities worldwide. Many existing rail networks still rely heavily on jointed tracks, particularly in freight yards, industrial railways, and secondary lines where welded rail solutions are less practical. Expansion of rail freight corridors and regional rail lines increases the need for track components such as fishplates. Maintenance and replacement demand is a major driver, as fishplates experience wear due to vibration, temperature changes, and heavy axle loads. Growth in mining and industrial railways also supports steady demand, as these applications often use jointed rails for operational flexibility and ease of repair.
Market Challenges
Despite consistent usage, the railway fishplate market faces challenges related to durability and performance under increasing load conditions. Fishplates are subject to fatigue, corrosion, and bolt loosening over time, which can compromise track integrity if not properly maintained. Higher train speeds and heavier axle loads increase stress on rail joints, accelerating wear. Environmental exposure, including moisture and temperature variation, can reduce service life, especially in regions with extreme climates. The gradual shift toward continuous welded rails in mainline networks also limits long-term growth potential. Ensuring quality consistency across different rail standards and gauges adds further complexity for manufacturers.
Market Opportunities
The market offers opportunities through material enhancement and design improvements. Development of high-strength steel and corrosion-resistant coatings improves fishplate durability and reduces maintenance frequency. Optimized designs that enhance load distribution and joint stability help address performance limitations of traditional fishplates. Growth of rail infrastructure in emerging economies presents long-term opportunities, as many new networks initially adopt jointed rails due to lower installation cost. Temporary track installations for construction and maintenance activities also create demand for reusable fishplate systems. Additionally, aftermarket replacement demand ensures continued market relevance even as welded rail adoption increases.
Regional Insights
Regional demand varies based on rail network type and maintenance practices. Asia-Pacific dominates the market due to extensive rail infrastructure in countries such as India, China, and Southeast Asia, where jointed rails are still widely used in secondary and freight lines. Europe shows steady demand driven by maintenance of existing tracks and use of fishplates in yards and sidings. North America maintains stable demand supported by freight rail operations and industrial rail systems. Africa and Latin America present growth opportunities as rail networks expand for mining, agriculture, and regional connectivity. The Middle East shows moderate demand linked to industrial rail and infrastructure development.
Future Outlook
The future of the railway fishplate market will be shaped by balancing traditional track systems with modern rail technologies. While continuous welded rails will dominate high-speed and mainline routes, fishplates will remain essential for specific applications requiring flexibility and ease of maintenance. Manufacturers will focus on improving durability, corrosion resistance, and load-handling capacity. Standardization across rail networks may simplify procurement and maintenance processes. As rail infrastructure investment continues globally, fishplates will remain a necessary component supporting track connectivity and operational reliability.
Conclusion
The railway fishplate market continues to play an important role in maintaining rail track integrity, particularly in jointed rail applications. Fishplates provide a practical and cost-effective solution for connecting rails and managing track loads. Although challenges such as wear and competition from welded rails exist, ongoing maintenance needs and infrastructure expansion support sustained demand. Through improved materials and design innovation, railway fishplates will remain relevant components within the broader rail infrastructure ecosystem.